Thermal imaging as an indicator of oil palm fresh fruit bunches: A review
Keywords:
ANN, k-Nearest Neighbor, Machine Learning, Oil Palm, Thermal ImagingAbstract
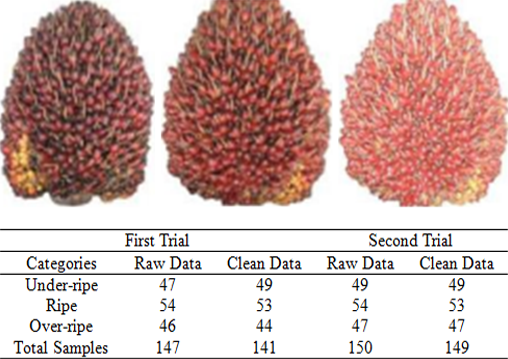
Thermal imaging is a non-contact, non-destructive method that records infrared radiation from the surface of an object to produce a temperature image. This research examines the use of thermal imaging alongside machine learning techniques, namely k-nearest neighbor (kNN) and artificial neural networks (ANN), to classify the maturity level of oil palm fresh fruit bunches. Thermal imaging data were analyzed to obtain the temperature difference as the main indicator in classifying the unripe, ripe, and overripe categories. Results showed that ANN provided higher classification accuracy (92.5% on test) than kNN (74.2% on test). Both methods proved the effectiveness of rapid, non-contact, and non-destructive ripeness assessment. These findings highlight the potential of integrating thermal imaging with advanced computational approaches to improve efficiency and accuracy in agricultural applications.