Improved positron generation via laser plasma interaction utilising target front surface architecture: A review
Keywords:
Bethe-Heitler, Laser Plasma Interaction, Particle-in-Cell, Positron, Target Surface StructureAbstract
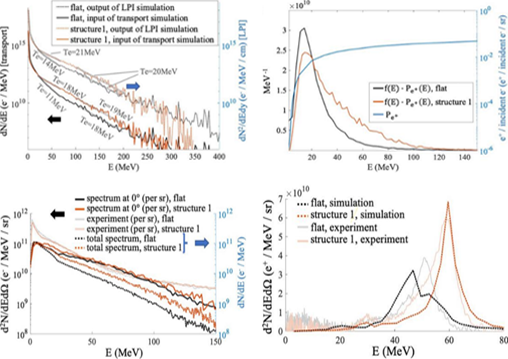
Positrons are electron antiparticles that are often produced in extreme astrophysical events, such as black holes and quasars. Positron production in the laboratory is typically done through plasma-laser interactions, utilizing the Bethe-Heitler process which involves the interaction of high-energy photons with the electromagnetic fields of atomic nuclei. One of the main challenges is to improve the efficiency of laser energy conversion into electron-positron pairs. This research utilizes a silicon microwire-based target surface structure to improve the positron production efficiency in laser plasma interactions. Particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations and experiments with the OMEGA EP laser system show that target structure 1 produces 50% more positrons than a flat surface target, with the conversion efficiency of laser energy to positrons increasing to 97%. This structure enables optimal laser energy focusing, resulting in efficient high-energy relativistic electrons to create electron-positron pairs. The results of this study show significant potential in the development of particle acceleration technology and applications in high-energy physics.