Energy storage device utilising garlic skin and carbon fibre derived from agricultural and industrial waste: A review
Keywords:
Carbon Fiber, Carbon Quantum Dots, Energy Storage, Garlic Skin, SupercapacitorsAbstract
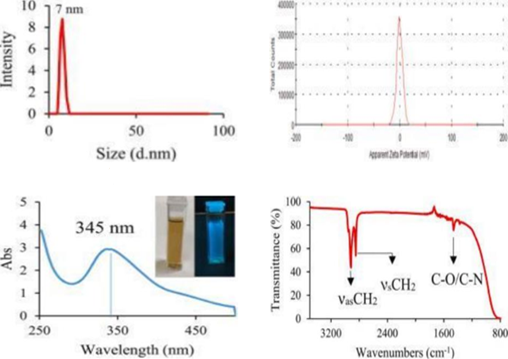
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are small-sized nanoparticles (1 – 10 nm) with unique properties such as high conductivity, thermal stability, and fluorescence capability, making them superior materials for energy applications. This research develops an energy storage device based on garlic skin waste and carbon fiber from agricultural and industrial waste. Garlic peel was processed into CQDs using pyrolysis method, while carbon fiber was obtained from methylcellulose. Analytical results showed that CQDs increased the specific capacitance of the gel electrolyte to 110.57 F/g, with excellent cycling stability reaching 96% after 2000 cycles. In addition, the carbon fiber-based electrode showed the highest specific capacitance of 155.58 F/g, energy density of 10.59 Wh/kg, and power density of 4047 W/kg, making it an economical alternative to carbon nanotubes and graphene. Material characterization via TGA, UV-Vis, FTIR, SEM, and TEM confirmed the high thermal stability and quasi-round particle morphology with an average size of 7 nm. The results of this study highlight the potential of CQDs from garlic skin as a sustainable solution for advanced energy storage applications.