Nano rod-shaped core-shell TiO2-SiO2 coating exhibiting superior self-cleaning capabilities under visible light: A review
Keywords:
Core-Shell, Photocatalytic, Self-Cleaning, TiO2-SiO2, Visible LightAbstract
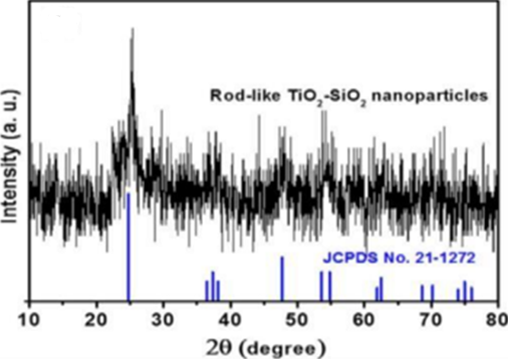
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a photocatalytic material widely used in self-cleaning applications due to its ability to decompose organic compounds with free radicals under UV irradiation. However, its limitations in stability and efficiency make it necessary to combine with other materials such as silicon dioxide (SiO2). This combination forms a core-shell structure where TiO2 becomes the active core, while SiO2 acts as a shell that improves stability, extends the absorption spectrum to visible light, and reduces particle agglomeration. This study examines the synthesis and characterization of rod-shaped TiO2-SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles that have superior self-cleaning ability under visible light. The synthesis was carried out using a modified hydrothermal method. Structure analysis using SEM showed uniform particle distribution, while XRD analysis confirmed the presence of anatase phase in TiO2. Self-cleaning evaluation was performed through methylene blue degradation and water contact angle measurement. Results show that this core-shell layer has better photocatalytic activity and hydrophilic properties than pure TiO2. With these characteristics, this material has great potential to be applied in environmental purification, waste treatment, and renewable energy technologies.