Biosynthesis and characterisation of silver nanoparticles utilising tin (Ficus carica) leaf extracts: A review
Keywords:
Ficus carica, Green Synthesis, Silver Nanoparticles, UV-Vis Spectroscopy, X-Ray DiffractionAbstract
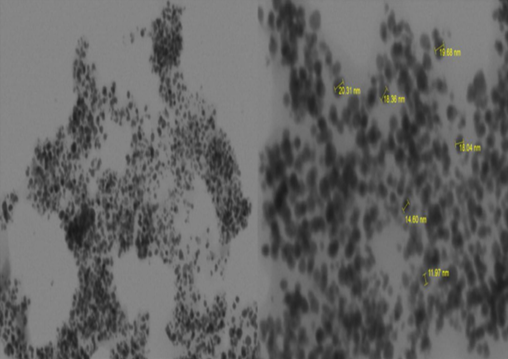
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are materials with various potential applications, ranging from catalysts to antibacterial agents. This study aims to synthesize and characterize AgNPs using tin leaf extract (Ficus carica) as a bioreduction agent in a green synthesis method. The synthesis process was carried out by utilizing AgNO3 as a precursor and evaluated using UV-Vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). UV-Vis results showed a characteristic absorption peak at a wavelength of 419 nm, indicating the successful synthesis of AgNPs. XRD analysis identified a face-centered cubic structure with an average particle size of 22.6 nm. STEM revealed a spherical particle morphology with sizes ranging from 11.97 – 20.31 nm. This green synthesis approach provides an environmentally friendly, efficient, and cost-effective solution in the production of AgNPs, with broad potential applications in the medical and technological fields.