Application of stereoelectroencephalography utilising single pulse electrical stimulation method for brain connectivity: A review
Keywords:
Brain, Connectivity Pulse Evoked Potentials, SEEG, SPES, Structural ConnectionsAbstract
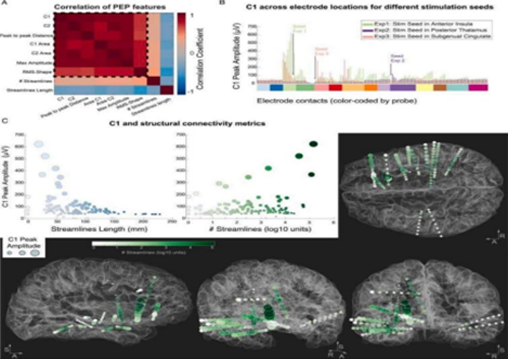
Stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) is a technique that allows direct observation of brain activity through electrodes implanted into the brain. This study utilized the single pulse electrical stimulation (SPES) method to explore brain connectivity structurally, functionally, and effectively. Results showed that SEEG with SPES was able to record pulse evoked potentials (PEP) indicating connections between neurons with high accuracy. Connectivity analysis identified PEP features, such as C1 peak amplitude, that significantly correlated with structural connection strength. However, connectivity models show limitations in areas with low connectivity or complex anatomy, such as brain sulci. In addition, the three-dimensional network topology showed improved conductivity resolution around the electrodes. This study underscores the need to improve methodologies to improve precision and resolution in brain connectivity assessment, as well as stimulation procedures.