Performance comparison of the Naive Bayes algorithm and the k-NN lexicon approach on Twitter media sentiment analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v3i2.229Keywords:
Classification, k-Nearest Neighbor, Lexicon, Naive Bayes Classifier, Sentiment AnalysisAbstract
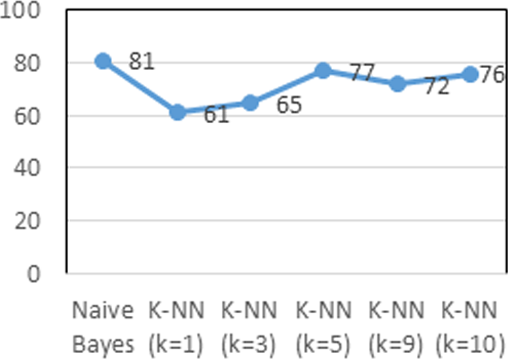
Sentiment analysis or opinion mining is a natural language that processes words to find out opinions, attitudes, or moods about certain things. Word processing in this study related to the process of classification in textual documents, which was classified into three classes, positive, negative, and neutral. Data obtained from social media Twitter were related to netizens' comments as many as 1000 comments. These data were crawled using keywords of the “Pilpres2019” and “Jokowi”. This study compared the performance of the Naive Bayes and k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) algorithms with the lexicon approach in classification. The aim of this study was to compare the level of accuracy, precision, and recall of Naive Bayes and the k-NN algorithm with the lexicon approach. From the evaluation, we concluded that the combination of the k-NN algorithm and the lexicon approach could improve accuracy in this sentiment analysis case. Generally, the k-NN algorithm with lexicon approach in which the k value is k = 5 has better performance with a 77% of accuracy level, followed by Naive Bayes with an accuracy of 81% of accuracy level.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Azhar Azhar, Siti Ummi Masruroh, Luh Kesuma Wardhani, Okfalisa Okfalisa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










