Analysis of anemia disease in Pakistan using logistic regression
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v5i2.281Keywords:
Anemia, Hemoglobin, Logistic Regression, Machine Learning, Public HealthAbstract
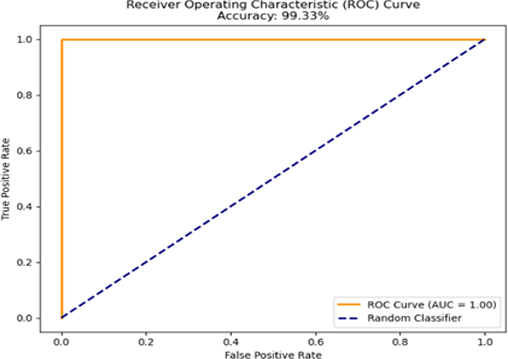
Anemia, a global health issue affecting over two billion individuals, is characterized by a deficiency in red blood cells or hemoglobin, impairing oxygen transport in the body. Early detection of anemia is critical, particularly in resource-constrained regions. This research aims to develop a robust anemia prediction model leveraging machine learning techniques and non-invasive data inputs, including red, green, and blue (RGB) pixel intensities and hemoglobin levels. The research focuses on three objectives which are to analyze the relationship between predictor variables and anemia status using a correlation heatmap, to assess the contribution of RGB pixel intensities and hemoglobin levels in predicting anemia using feature importance analysis, and to identify significant predictors through recursive feature elimination. The model, developed using logistic regression, achieved an exceptional accuracy of 99.33% and an AUC score of 1.00. The hemoglobin level emerged as the most significant predictor, showing a strong negative correlation of -0.84 with anemia status. This approach not only enhances understanding of anemia's determinants but also provides actionable insights for healthcare professionals to devise targeted therapies and public health measures. Addressing these risk factors is vital to improving health outcomes, particularly for vulnerable populations at higher risk of anemia.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Agnes Lee Si Tian, Kang Yuan Chin, Nik Azlin Nik Aziz, Norhaidah Mohd Asrah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










