Physical and electrochemical properties of activated carbon derived from bamboo charcoal utilizing diverse electrolytes for supercapacitor applications: A review
Keywords:
Activated Carbon, Bamboo, Electrochemical, Specific Capacitance, SupercapacitorsAbstract
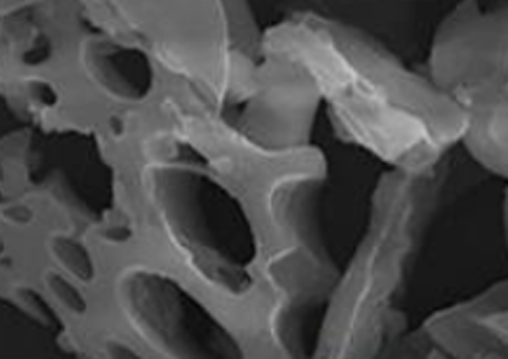
Activated carbon is a highly porous material that is widely used in energy applications, such as supercapacitors, as it has a large specific surface area and good electrical conductivity. Bamboo, as one of the abundant biomasses, can be processed into high-quality activated carbon through chemical activation process. With its natural carbon-rich structure and pores, bamboo provides a great opportunity to improve the energy storage performance of supercapacitors. This study analyzes the physical and electrochemical properties of activated carbon synthesized from bamboo charcoal using KOH activation for supercapacitor applications. Structural characterization was performed using X-ray diffraction and field emission scanning electron microscopy, which showed an amorphous structure with high porosity. Electrochemical studies via cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge-discharge revealed that the electrolyte mixture (Na2SO4 1 M and KOH 0.5 M) yielded the best performance with a maximum specific capacitance of 290 F/g at a current density of 1 A/g. These results indicate that bamboo-based activated carbon has great potential for environmentally friendly energy storage applications.