Characteristics of human voice vibrations based on FBG strains
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v4i2.257Keywords:
Chirped FBG, FBG Uniform, Fiber Bragg Grating, Optical Interrogator, StrainAbstract
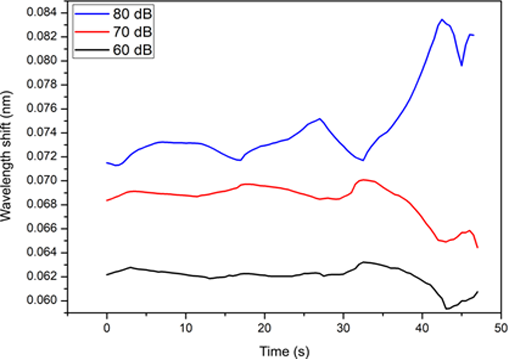
FBG is widely developed as a sensor in its application as a sensor, FBG is commonly used either in industry or in clinical applications to measure changes in physical parameters such as pressure, strain, temperature, and corrosion, as well as to monitor the body's heartbeat and breathing. This research uses 2 types of FBG, namely uniform and chirping. The spectrum used is in the range of 1550 nm. Using an optical sensing interrogator as a tool to read wavelength changes as well as input and output with an infrared laser light source. This study aims to analyze the response of FBG sensors to human voice vibrations with variations in the intensity of sound violence. The results showed that at a hardness intensity of 60 dB using a uniform FBG with a reflectivity of 10% experienced a wavelength change of -0.0304 nm, at an intensity of 70 dB 0.0304 nm, and an intensity of 80 dB experienced many wavelength changes 0.06669 nm. The greater the intensity of the sound, the more FBG response shows an increase in wavelength. The largest strain value detected by the uniform FBG with 10% reflectivity is at 70 dB intensity of 5.5579 × 10-5 strain while the lowest value is at 80 dB intensity of 4.4816 × 10-5 strain. The chirping FBG with 10% reflectivity has the highest strain value at 70 dB intensity with a respective strain value of 1.18 × 10-4 strain. Giving sound vibrations such as some of A, I, U, E, and O to FBG is useful for calculating how the transmission peak of FBG shifts due to strain. When the object emits sound vibrations with a certain intensity, the pressure that occurs will be more than the object when it is at rest, so the greater the sound vibration, the greater the strain that occurs.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Rani Nurpadilla, Bunga Meyzia, Saktioto Saktioto, Mohammed M Fadhali

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










