Effect of ultraviolet radiation on total electron content in global positioning system observations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v4i3.267Keywords:
Extreme Ultraviolet, GPS, Ionosphere, Solar, Total Electron ContentAbstract
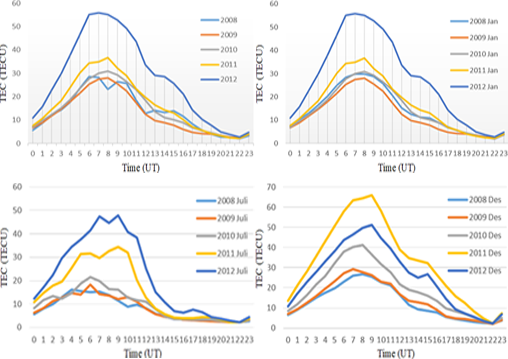
Climate is one of the basic elements for understanding natural phenomena and the development of civilizations throughout history. Climate change determines most of the modifications of human nature and culture, as human must adapt to changing conditions which are sometimes an important element that can enhance or threaten its existence. This study aims to determine the characteristics of changes in the total electron content (TEC) and determine the radiation has influence to TEC through observing the global positioning system (GPS) in the ionosphere. In addition, the TEC is a measure of ionospheric parameters that affect the radiation that occurs. This study uses secondary data obtained from the Cibinong Spatial Global Station in 2008 – 2012. This research was conducted as a comparison of the TEC and extreme ultraviolet (EUV). The method used is a simple statistical method which seeks the maximum and minimum the TEC and EUV data, as well as the correlation method to relate the coefficient of determination TEC and EUV. As the results the maximum TEC value is 55.895 TECU which occurred in 2012 at 7 unit time (UT) and the minimum TEC value is 1.955 TECU which occurred in 2010 at 22 UT. The correlation ratio between the TEC and EUV is directly proportional, where the higher the value of the TEC, the higher the EUV value. In closing, TEC and EUV are influence by solar activity.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Fauzan Iqbal, Asnawi Husein, Nur Aisyah Arifin, Vepy Asyana

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










