Microwave media simulation to generate nitrogen plasma at atmospheric pressure
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v2i1.209Keywords:
Cutoff Frequency, Electric Field, Microwave, Nitrogen Plasma, Transverse ElectricalAbstract
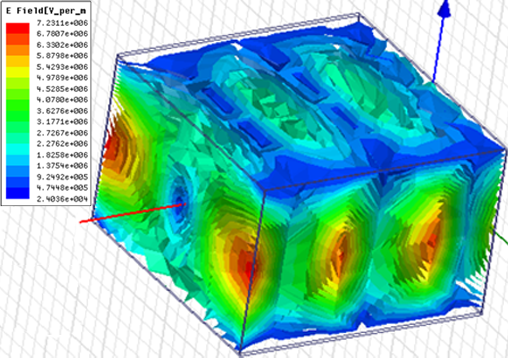
The development of methods to generate artificial plasma continues to be carried out for industrial purposes in machines and production products. To overcome experimental problems in modeling development, various methods have been carried out. One of the methods used is to simulate the air in a microwave oven. This simulation will describe the electric field distribution of each mode to identify the plasma by introducing the cutoff frequency. Ionization gas with a composition of 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, and 1% other gases at a pressure of 1 atm. The microwave oven chamber is made of an iron conductor in the form of a beam with dimensions 29 × 29 × 19 cm3, with a continuous supply of 800 W and 220 V. Power loss as a function of frequency shows the cutoff frequency using an S-parameter graph and electric field distribution as a function of position in each mode. The plasma formed is in modes 20, 01, and 11 because the electric field exceeds the breakdown voltage value to generate plasma, which is 6 × 106 V/m. The bigger the electric field, the more plasma is produced, which is indicated in the mode positions in the microwave oven.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Muhammad Fauzan, Reeky Fardinata, Khaikal Ramadhan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










