Water seepage rate in composted soil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v3i3.236Keywords:
Compost Soil, Floating Voltage, Soil Permeability, Water Infiltration Rate, Water SeepageAbstract
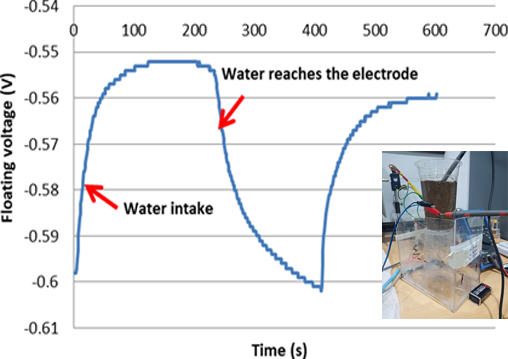
Water infiltration is one important factor for plant growth. Water that cannot seep into the pores of the soil creates a pool of water so that soil permeability is low. From these conditions, it is necessary to conduct research to determine the rate of water seepage in the soil. This study aims to analyze. The rate of water seepage on the ground by utilizing the difference in floating voltage. Based on the difference in floating voltage, two-dimensional modeling of the stress distribution and the distribution of water infiltrate time into the ground using the method of adding water repeatedly. The sample in this study consisted of 2 types of soil, compost and sand. Land with high permeability can increase the rate of infiltration thereby reducing the rate of water. The results of this study concluded that the pore size and particle arrangement greatly affect the rate of water seepage.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Zulkarnain Zulkarnain, Rizka Kurniawati, Triwulandari Triwulandari, Ikhsan Rahman Husein, Ridho Kurniawan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










