Wavelength dependence of optical electronic nose for ripeness detection of oil palm fresh fruits
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v2i3.212Keywords:
LED-Photodiode Sensor, Oil Palm Fruits, Optical Electronic Nose, Ripeness, WavelengthAbstract
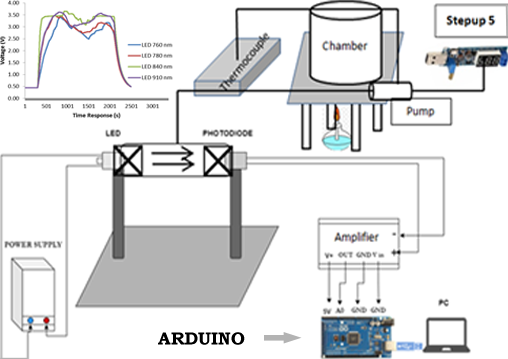
Electronic noses have been developed as an artificial sense to imitate the human nose based on volatile gases. They have been used in agriculture to monitor and predict fruit qualities such as ripeness and chemical contents. Electronic noses with semiconductor gas sensors have a limitation of volatile gases detected. Therefore, optical electronic noses using an output coupler become an alternative due to the wavelength dependency of the gas types. The ripeness of oil palm fresh fruit bunches (FFBs) is one of the main factors in determining the quality of crude palm oil. Electronic detection is preferable to substitute the manual methods for ripeness detection. This study built an optical electronic nose and analyzed the wavelength dependence on the detection performance. The electronic nose consisted of an infrared LED and a photodiode enclosed in a chamber, a microcontroller, and a sample chamber. We tested four infrared LEDs with 760, 780, 840, and 910 nm wavelengths. The samples were fruitlets taken from oil palm FFBs, previously categorized as unripe, ripe, and overripe. The fruits were grounded, inserted into the sample chamber, and preheated to increase the volatile gas concentration. Trapezoid areas represented the time-varying output voltages for each LED. The results showed that overripe fruits had slightly higher trapezoid areas. LED of 840 nm wavelength obtained higher trapezoid areas. LED of 780 nm was the best candidate for the electronic nose due to linearity in increasing trapezoid areas. The results showed the potential of the optical electronic nose for oil palm fruits.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Ikhsan Rahman Husein, Minarni Shiddiq, Dewi Laila Sari, Annisa Putri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










