Properties of BaTiO3 nanoparticles based on FTIR derived using Nephelium lappaceum L. leaf extract
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v4i3.268Keywords:
BaTiO3, Doping, FTIR, Functional Groups, Nephelium lappaceum L.Abstract
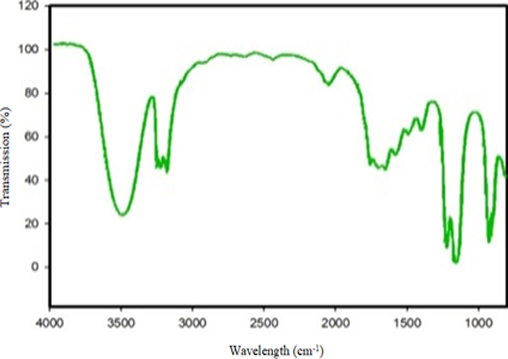
The properties of barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanoparticles synthesized with rambutan leaf extract (Nephelium lappaceum L.) were analyzed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) characterization techniques. Rambutan leaf extract contains bioactive compounds that have the potential to enhance unique physical and chemical properties. This study aims to analyze the properties of the nanoparticles and to characterize the functional groups present in BaTiO3 nanoparticles synthesized using rambutan leaves. The nanoparticle synthesis process involved extraction, followed by the preparation of a BaTiO3 solution and doping. The FTIR spectrum displayed characteristic peaks identifying the presence of functional groups. The results indicated that the region 3500 – 3200 cm-1 corresponds to O–H groups (alcohol and phenolic), the region 1700 – 1600 cm-1 to C=O groups (carbonyl), the region 1600 – 1500 cm-1 to C=C groups (alkene), and the region 1200 – 1000 cm-1 to C–O groups (ether). Each functional group exhibits distinct properties.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Rahmi Dewi, Yanuar Hamzah, Yohana Manik, Friska Ziliwu, Norsinta Ida Simbolon, Hidayati Syajali, Shintya Maulidya, Yunita Ningrum, Harum Fatanah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










