Green-synthesized ZnO and Ag nanoparticles: A comparative study of optical, morphology and structural properties for photocatalytic applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v5i3.307Keywords:
Annona muricata, Nanoparticles, Photocatalytic, Silver, Zinc OxideAbstract
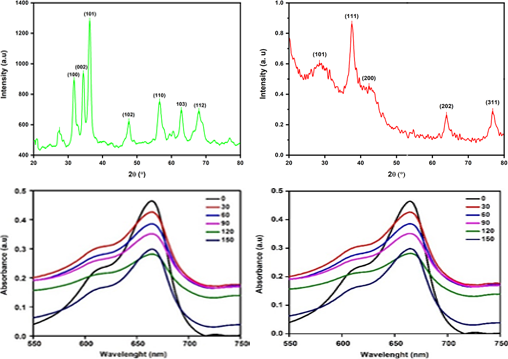
In this study, zinc oxide (ZnO) and silver (Ag) nanoparticles were synthesized using Annona muricata leaf extract as a reducing and stabilizing agent with variations in the molar ratio of 1:3, 1:5, and 1:7. Optical characterization using UV-Visible spectroscopy revealed that the variations of molar ratio influence the absorption peak and band gap energy of the resulting ZnO and Ag. UV-Vis results show that the molar ratio 1:5 was optimal for synthesizing ZnO and Ag. The band gap value of synthesized ZnO and Ag at a 1:5 molar ratio was 3.27 eV and 2.01 eV, with absorption peaks at 355 nm and 435 nm respectively. XRD characterization shows that ZnO nanoparticles has a hexagonal wurtzite structure with lattice parameters of a = 76 Å and c = 4. 95 Å and for Ag nanoparticles has a face centered cubic structure with lattice parameters a = b = c is 4.15 Å. Annona muricata leaves extract shows photocatalytic properties that can be applied to the degradation of polluted water. This shows that ZnO nanoparticles via green synthesis using Annona muricata leaf extract is a very simple, low-cost and environmentally friendly method.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yanuar Hamzah, Tengku Emrinaldi, Rahmi Dewi, Ari Sulistyo Rini, Lazuardi Umar, Mediniah Putri Simatupang, Rabiah Rabiah, Muhammad Deri Noferdi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










