Effect of holding time on optical structure properties of Ba(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 thin film using sol-gel method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v1i2.28Keywords:
Crystal Structure, Energy Gap, Holding Time, Sol-Gel Method, Thin Film BZTAbstract
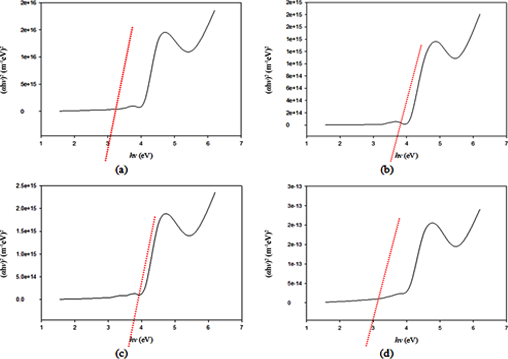
The ferroelectric thin film material of barium zirconium titanate (BZT) on the fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass substrate was successfully prepared using the sol-gel method. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of crystal size on the variation of holding time. The lattice parameter data has a value of a = b of 3.918 Å and for c it is 4.01 Å. The results of this study indicate that the crystal structure of BZT is tetragonal because the lattice parameter has the same values a and b but not equal to c. To obtain the bandgap energy, a thin film plot method of Ba(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 was used at a temperature of 700°C with a holding time of 30 minutes, 1 hour, 1 hour 30 minutes, and 2 hours. The optical thin layer bandgap energy of Ba(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 was calculated using the Tauc plot. The absorbance values obtained were 3.277, 3.0654, 3.323, and 3.424 a.u. The maximum transmission (TM) occurs at 1 hour holding time which gives a percentage of TM1 44.477% and TM2 20.568%. While the 2 hour hold time gives a minimum transmission (Tm) of Tm1 10.859% and Tm2 7.759%, respectively.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Taufiq Hidayat, Rahmi Dewi, Yanuar Hamzah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










