Plasma argon particle interactions in a non-equilibrium state through the Maxwell-Boltzmann kinetic equation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v5i2.272Keywords:
Argon, Density, Distribution, Non-Thermal, PlasmaAbstract
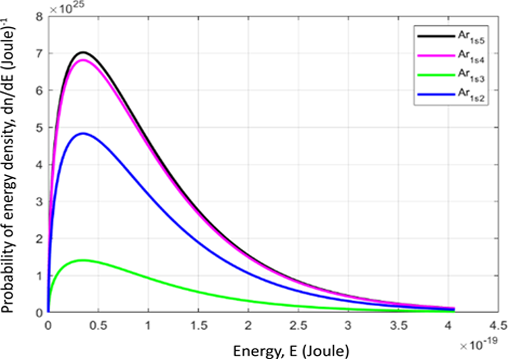
Non-thermal argon plasmas serve multiple functions, particularly in healthcare and industrial applications. Numerous particles of the same species exhibit varying velocities, referred to as a population. The distribution function is a standard method for characterizing a population. The speed and energy distribution functions in the Maxwell-Boltzmann equation are simulated utilizing MATLAB. The density of each species was numerically calculated using the Runge-Kutta method. This research reviews various argon species, including Ar*, Ar+, Ar(1s5), Ar(1s4), Ar(1s3), Ar(1s2), Ar, and electrons. The parameters utilized include a pressure of 10 mTorr, an argon temperature about 400 K, and an electron temperature about 30,000 K. The maximum velocity probability density value is observed in the Ar+ species at 6.18 × 107 (m/s)-1, while the minimum value is found in electrons at 1.93 (m/s)-1. The maximum energy probability density value is observed in the Ar+ species at 2.13 × 1029 (Joule)-1, while the minimum value is found in the Ar(1s3) species at 1.40 × 1025 (Joule)-1. The time evolution of the distribution function, independent of the coordinates r, is associated with v, at t = 10-8 s. The velocity distribution function is significantly affected by the density value, while the distribution function is contingent upon the velocity.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Azza Ronald, Saktioto Saktioto, Kusherbayeva Maikul, Kushkimbayeva Bibara, Mohd Rendy Samudra, Dedi Irawan, Hewa Yaseen Abdullah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










