Design and optimization of square SRR metamaterial-based microstrip antenna for wideband biomedical sensing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v6i1.331Keywords:
Antenna Optimization, Biomedical Application, Microstrip Antenna , SRR Metamaterial , Wideband SensingAbstract
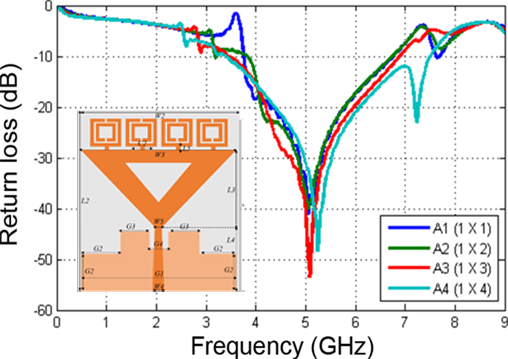
The continuous advancement in wireless biomedical technology necessitates the development of compact, high-performance antennas capable of operating across a wide frequency range. In this context, this study reports the design and optimization of a square split-ring resonator (SRR) metamaterial-based microstrip antenna to enhance bandwidth and gain characteristics for wideband biomedical sensing. The proposed metamaterial, composed of one to four square SRR unit cells, was modeled using copper patches on an FR-4 substrate with a dielectric constant of 4.3 and simulated in CST Studio Suite 2019 over a frequency range of 0.009 – 9 GHz. The electromagnetic behavior of the structure was analyzed through S-parameter characterization, and the Nicolson–Ross–Weir (NRW) retrieval method was applied to extract the effective constitutive parameters, including relative permittivity, relative permeability, and refractive index. The optimized four-cell SRR configuration demonstrated double-negative (DNG) characteristics, exhibiting a relative permittivity of -153.65, a relative permeability of -8.85, and a refractive index of -9.48, thereby confirming the negative-index properties essential for enhanced electromagnetic field confinement and energy concentration. Integration of the optimized metamaterial into the microstrip antenna structure yielded significant performance improvement, achieving a return loss of -48.31 dB, bandwidth of 4.37 GHz, and gain of 2.23 dBi. These results substantiate that the square SRR metamaterial contributes to superior impedance matching and field localization, making the proposed antenna architecture highly promising for wideband biomedical sensing and potential internet of things (IoT) healthcare implementations.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Saktioto Saktioto, Cici Yana Tasya Angraini, Yan Soerbakti, Ari Sulistyo Rini, Syamsudhuha Syamsudhuha, Sofia Anita

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










