Acoustic wave propagation model in the surface layer area based on the Runge-Kutta method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v3i2.227Keywords:
Acoustic Modelling, Gradient, Runge-Kutta Method, Surface Layer, Transmission LossAbstract
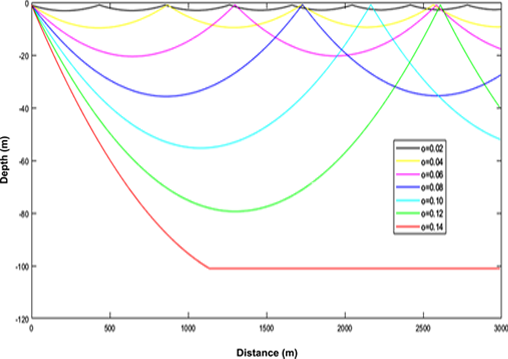
Simulation of acoustic wave propagation in the surface layer area is carried out by taking a positive value acoustic velocity gradient so that in this simulation there will be a wave phenomenon trapped in the surface layer area. In this study, acoustic beam emission was conducted by varying the angle of incidence and length of the beam used, and the determination of the acoustic velocity gradient was carried out using the Runge-Kutta order of order 2. The results showed that at depths of 0 to 40 meters with an acoustic velocity of 1405 m/s, for a length of 1 meter and a gradient pattern of +2.5 obtained a minimum angle of incidence of 0.09 radians with a wave propagation of 250 meters. Comparison between analytical and computational results on wave propagation in the surface layer area is a 4.51% error.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Defrianto Defrianto, Hazmi Wirianto, Usman Malik

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










