Determination of the shadow zone area in the ocean computationally by simulating the propagation of acoustic rays
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59190/stc.v3i2.228Keywords:
Acoustics, Gradient, Propagation, Shadow Zone, Sound SpeedAbstract
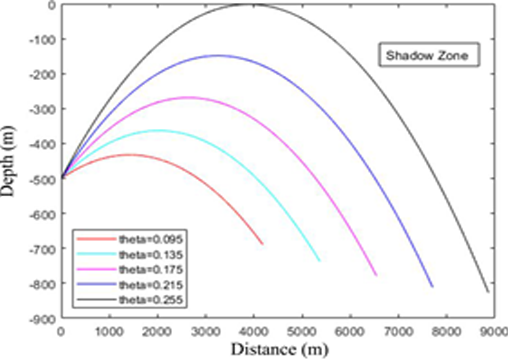
Simulation of acoustic wave propagation to determine the shadow zone area using computational methods has been carried out using negative value gradients. The study was conducted by varying the angle of incidence and variations in the length of the beam used. This research was conducted by comparing analytical results with computational results. The results of this study indicate that at a depth of 500 meters with a sound speed of 1493.1 m/s, a beam length of 1 meter, and a gradient pattern of -0.1, a maximum angle of 0.255 radians is obtained with the shadow zone area being at a depth of 0 to 800 meters and a distance of 5000 meters of wave source. The value of the difference or error in analytical data and computational data is 0.0817%.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Defrianto Defrianto, Nando Pratama, Usman Malik

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










